What you must remember :
- We speak of diarrhea when there are frequent (more than three times a day) and abundant liquid or soft stools.
- Acute diarrhea can be of infectious, physiological or hormonal origin.
- The origins of a stomach ache with chronic diarrhea are numerous: food intolerances, medications or even irritable bowel syndrome.
- Solutions exist to relieve and prevent the occurrence of stomach aches and diarrhea (diet, hydration, probiotics, etc.).
Stomach aches and diarrhea are common gastrointestinal disorders that can disrupt our daily lives. They can have various origins. In this article, we will reveal to you the reasons why we are prone to these ailments, the solutions to relieve and prevent them, as well as the right actions to take based on your symptoms.
Why are we prone to stomach aches accompanied by diarrhea?
Stomach aches and diarrhea can be the result of a variety of factors. We speak of diarrhea when there are frequent (more than three times a day) and abundant liquid or soft stools. This disorder is generally accompanied by pronounced stomach aches such as cramps , spasms or even nausea. There are two types of diarrhea: acute diarrhea which is occasional and often caused by viral or bacterial infections, and chronic diarrhea which persists over time and can result from various causes such as chronic digestive disorders or inflammatory diseases.
The origins of a stomach ache with acute diarrhea
Diarrhea and stomach aches can occur due to infections, psychological or hormonal factors.
Infectious origins
Infectious origins are one of the main reasons for stomach aches and acute diarrhea. Pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria and parasites, can enter the gastrointestinal system and disrupt its normal functioning. Viral gastroenteritis or food poisoning are common examples of gastrointestinal infections.
These pathogens are often transmitted through consumption of contaminated food or water, as well as close contact with infected people. Symptoms include abdominal pain, cramps, nausea, vomiting and severe diarrhea. The infection can last from a few days to several weeks, and dehydration can be a serious risk, especially in young children and the elderly.
Physiological origins
Certain physiological situations can also trigger a stomach ache and diarrhea. Food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity, can lead to unpleasant gastrointestinal symptoms. The intestine cannot process these substances properly, leading to unpleasant symptoms. Additionally, certain illnesses, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), can lead to abdominal pain and episodes of diarrhea or constipation. Dietary factors and stress can also influence the occurrence of these symptoms. Indeed, it is well known that periods of stress or nervousness are synonymous with diarrhea and stomach aches in certain people. The expression “having a knot in my stomach” also perfectly reflects this phenomenon.
Hormonal origins
Hormones play an important role in regulating body functions, including digestion. In women, hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can influence how the digestive system functions. Some women experience abdominal pain and episodes of diarrhea shortly before or during their period. Although the exact mechanisms are not completely understood, it is clear that hormones impact intestinal motility and sensitivity.
The origins of a stomach ache with chronic diarrhea
If symptoms of stomach ache and diarrhea persist for several weeks or become recurring, it may indicate more complex underlying problems. Here are several examples of situations or illnesses that can be responsible for stomach aches and diarrhea in the long term.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can disrupt the balance of normal intestinal flora, which can cause imbalances in the digestive system and lead to stomach aches and diarrhea.
- Food intolerances: Food intolerances, such as lactose or gluten intolerance, occur when the body has difficulty digesting specific food substances. They are present in both children and adults. They can cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as stomach aches, bloating and diarrhea after consuming foods containing them. Blood tests can help determine the exact origin of these symptoms.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): IBS is a functional disorder of the digestive system which is characterized by recurrent stomach aches and transit disorders (diarrhea or constipation). The exact cause is unclear, but stress, diet and increased intestinal sensitivity are possible factors.
- Crohn's disease: It is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect the entire digestive tract. It causes chronic inflammation of the intestinal wall. This inflammation can cause intense stomach aches, frequent diarrhea and rectal bleeding. Symptoms can vary in intensity and often require ongoing medical treatment to manage the inflammation and relieve symptoms.
Our advice to relieve and prevent stomach aches with diarrhea
When stomach aches and diarrhea occur, it's important to take steps to relieve the symptoms and minimize their impact on your well-being. Don't panic, we're here to guide you! Here are our few tips:
1 – Ensure good hydration
Diarrhea causes a significant loss of water and electrolytes through the stool. To prevent dehydration, it is essential to drink plenty of water and hydrating liquids such as broth and herbal teas. If you cannot tolerate liquids due to nausea, take small, frequent sips. It is essential to make sure you stay hydrated .
2 - Adopt a diet that is gentle on your stomach
When you experience stomach aches and diarrhea, choose foods that are soft and easy to digest. This could be, for example, cooked rice, bananas, unsweetened applesauce. Be sure to avoid fatty, spicy, and high-fiber foods, as they can make symptoms worse. Also avoid irritating foods and drinks that can increase abdominal discomfort and bowel movement frequency.
3 – Take a course of probiotics to strengthen your intestines
Probiotics , present in certain yogurts and food supplements, can help restore the balance of intestinal flora and promote better digestion. They can be particularly useful after a gastrointestinal infection to help restore gut health and regain vitality. So consider integrating digestive probiotics to help you on a daily basis.
At DIJO, we have created the Essential Probiotics cure , which aims to repopulate your intestines with good bacteria, and strengthen your intestinal microbiota . These quality bacteria promote regular intestinal transit and improve the consistency of stools, to relieve diarrhea and stomach aches.
4 - Over-the-counter medications, with medical advice
Over-the-counter antidiarrheal medications can help slow bowel movements and reduce the frequency of bowel movements. However, these medications should not be used excessively, as they may prolong an infection or underlying illness. Be sure to consult a healthcare professional before using any medication.
What to do based on stomach pain and bowel movements?
Depending on the severity of the symptoms and the nature of the stools, here are the actions to consider:
-
Mild symptoms: If the stomach ache and diarrhea are mild, it is usually possible to manage them at home by following the tips mentioned above.
-
Serious symptoms: If you experience severe abdominal pain, high fever, blood in the stool, or dehydration, consult a healthcare professional.
- Chronic symptoms: If symptoms persist or recur frequently, consult a doctor for a thorough diagnosis and proper treatment plan.
Below you will find a detailed table of possible situations and the associated procedure:
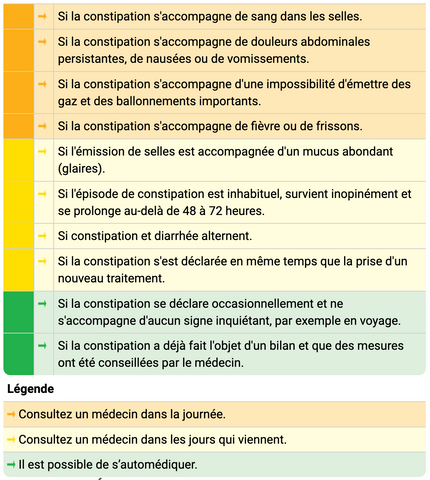
Image source: https://www.vidal.fr/immobiliers/astronomie-intestins/mal-ventre-adulte/que-faire.html













